Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Before we get familiar with shoulder replacement surgery it is important to understand the anatomy of shoulder. The human shoulders are built with three bones, the upper arm bone or humerus, the shoulder blade or scapula and the collar bone or clavicle. Shoulder works like a ball-socket joint. The head of the upper arm, much like a ball fits into shoulder blade’s shallow socket called the glenoid. Articular cartilage, a smooth substance covers the bone surfaces that touch to ensure an easy movement. The other bones are however covered by a thin, smooth tissue known as the synovial membrane. For a normally operating shoulder joint, the membrane secretes small amount of fluids to lubricate the cartilage thereby, eliminating all sorts of frictions in the shoulder.
The tendons and muscles around the shoulder provide support, strength and stability and all these structures together enable the shoulder to rotate at a much higher range than any other joint.
Symptoms of shoulder arthritis:
Some usual symptoms for doctors to diagnose shoulder arthritis are:
- Severe unbearable shoulder pain obstructing everyday actions and activities like reaching out something at a height, washing, pulling things, etc,
- Significant paid at rest time preventing a comfortable and good night sleep.
- Weakness, stiffness and loss of motion/movement at shoulder joint.
Need for shoulder replacement
Multiple medical conditions causing severe shoulder pain and disability are the reasons for doctors to recommend a shoulder replacement surgery.
Some of these include:
- Osteoarthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease): Occurring mostly among people of 50+ age, this is the usual and most common “wear and tear” arthritis. The cartilage which acts as a cushion between the shoulder bones becomes soft and gradually wears away over time. This leads the bones to rub against one another and consequently, the shoulder becomes stiff and painful. With no ways of prevention, this is the most common reason for shoulder replacement.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: when the synovial membrane surrounding the shoulder joint gets inflamed and thick. Persistent inflammation can damage the cartilage and leads to loss of cartilage, stiffness and pain.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: A severe shoulder injury that tears off the tendons or ligaments could damage the articular cartilage over time leading to pain and limited shoulder movement.
- Patients with long-held rotator cuff tear can cause cuff tear arthropathy due to changes in the shoulder joint caused by rotator cuff tear.
Types for shoulder replacement surgeries
Being highly technical, shoulder replacement is performed by a highly experienced surgical team. There are multiple types of shoulder replacement surgeries and the surgeon decides on the type to b performed based on the patient’s condition and health needs.
- Total Shoulder Replacement: A total shoulder replacement surgery typically involves the replacement of the arthritic joint surfaces with perfectly polished metal balls fixed with a stem and plastic socket. The best patients for total shoulder replacement include are the ones with osteoarthritis and intact rotator cuff tendons.
- Stemmed hemiarthroplasty: the procedure in which on the ball is replaced from the shoulder is called hemiarthroplasty. Traditionally the surgery involves the replacement of the humerus head with a metal ball and stem and is called stemmed hemiarthroplasty. This is suggested by the surgeon usually when the humeral head is fractured but the socket is fine.
- Resurfacing Hemiarthroplasty: this surgery involves just the replacement of joint surface of the humeral head with a prosthesis and without a stem. It preserves the bones and hence is an alternative to the stemmed shoulder replacement for shoulder arthritis patients.
- Reverse total shoulder replacement: in reverse total shoulder replacement they switch the socket and the ball positions. This means that the plastic socket is attached to the upper arm and the metal ball to the shoulder bone. The patient can lift their arm with the use of deltoid muscle instead of a torn rotator cuff.
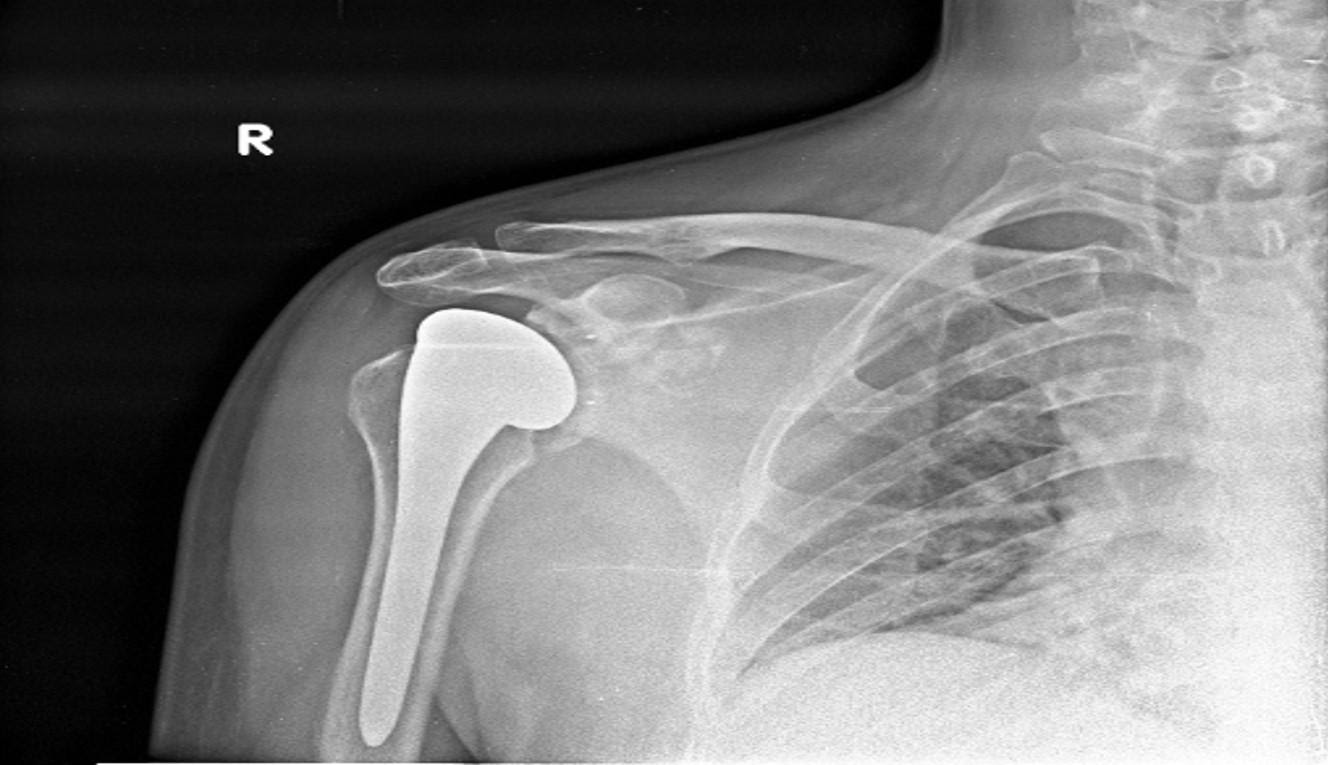
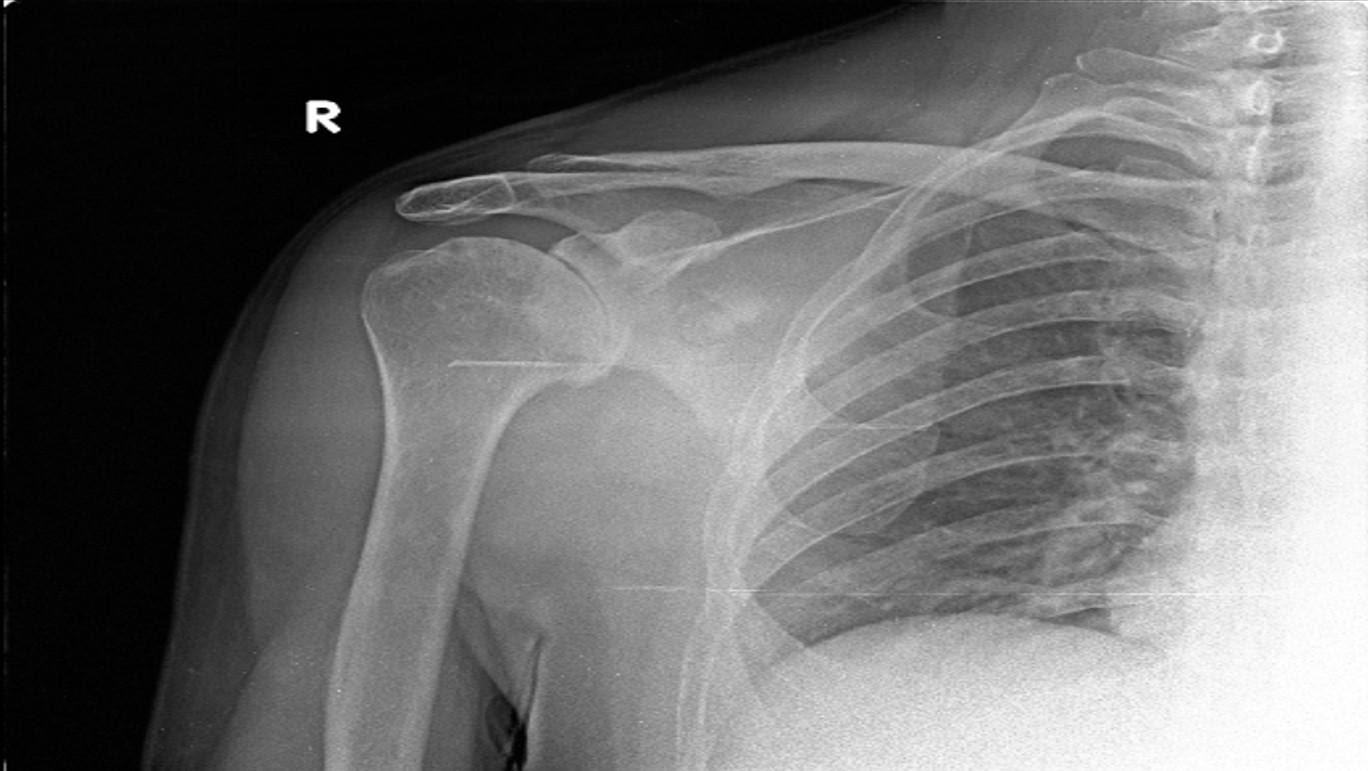
Preparation for shoulder replacement and precautions
Deciding on the shoulder replacement surgery the patient is usually suggested to have a complete physical examination several weeks before surgery to ensure if they are healthy enough to undergo surgery and recover from it. There is a mandatory obligation for the patients to disclose all their medications and stop/ continue them before or after surgery as suggested by the surgeon and doctors. It is advised to avoid trying to reach high shelves and take help for chores like dressing, bathing, cooking, etc during the first few weeks.
Process of shoulder replacement surgery:
On being admitted to the hospital on the day of surgery, patients are first dealt with by the anaesthesiologist in the preoperative preparation area. The surgeon and the anaesthesiologist decide on the type of anaesthesia to be used. It could be general anaesthetic (full body numb), regional anaesthetic (numbing the place of surgery) or a combination of both.
In the surgery procedure, the shoulder joint is replaced with an artificial device called prosthesis. The procedure involves either replacing the humerus bone, the ball or both the ball or the socket. The procedure takes about 2 hours depending upon the type of surgery to be performed.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Prophylactic antibiotics are given to prevent any infection. The patient is usually discharged within a day or two, allowed to eat solids and move out of bed. Some post-surgery pain is a normal part of the healing process but the pain specialists team will continuously monitor the patient and keep the patient comfortable while in the hospital and the oral medications are given to control pain after discharge from the hospital. Physical therapy begins soon after surgery, once the pain subsides, for the patient to gradually regain the shoulder strength and movements. On discharge, the shoulder is hung by a sling which stays for the initial 2 to 4 weeks of recovery. Soaking the wound in water is to be avoided until its sealed and dried and following surgeons home exercise plan is mandatory.
Outcomes of shoulder replacement
Once the recovery phase smoothly completes, with complete adherence to doctor’s post-recovery recommendations, patients can have near normal function and good painless movement.
